Tutorial 02: Heat Transfer analysis of earth air tunnel heat exchanger (EATHE) using OPEN-FOAM
Figure 2.1 (a) Temperature Contour of EATHE domain with BCs
Figure 2.1 (b) Meshed domain of EATHE section
Problem Identification
In this problem investigation of EATHE using OPENFOAM is proposed for heat transfer modeling, in which air is flow in EATHE section from one inlet condition, which is assumed at surface of soil structure (See the following figure). Air properties are selected from literature available in digital medium. Outlet is at top of the room which is selected for cooling effect of EATHE system. Some assumptions are applied in this problem like soil temperature is assumed at constant value for this problem. Air properties are also assumed constant for this problem.
“buoyantBoussinesqPimpleFoam” is selected as solver for this problem. Open Foam software is installed on Win 7, provided by FSD blueCAPE Lda: http://bluecfd.com/
Note: This tutorial is not endorsed/ supported by provider of software's which are used in this tutorial. This tutorial is made for educational purpose only.
Figure2.2 Different Boundary Conditions
The simulation is solved for ambient conditions at transient flow scheme available in selected solver.
Pre-Processing
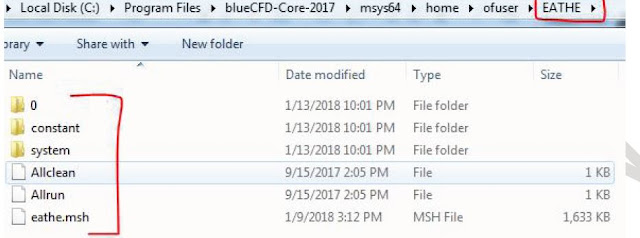
This problem is selected as turbulent flow problem, so the solver must have capability to solve turbulent flow conditions, that’s why “buoyantBoussinesqPimpleFoam” is selected as solver. The very first step is import suitable mesh file in open-foam software. There are various methods available in software to read mesh file, but we use “fluentMeshToFoam” command to read *.msh file generated by Ansys Fluent software. It is required to make a folder in home directory (Folder Name EATHE) of your open-foam software, where important sub-folders are already presented (see the following figure)
Figure 2.3 Folder in home directory for this tutorial
After desired folder creation, run open-foam software (see the following figure)
Figure 2.4 Run Open-Foam using blueCFD terminal
Run “ls” command in this terminal to verify the user created folder (see the following figure)
Figure 2.5 ls command to check the folders in home directory
After verification of user folder (EATHE), run “cd” command to enter in this folder (see the following figure)
Figure 2.6 cd command to enter desired folder
Run “fluentMeshToFoam” command in terminal (see the following figure), it must be ensure by user that msh file is available in main folder by run command “ls” again, in this tutorial eathe.msh file is used (copy from tutorial available in Google drive link)
Figure 2.7 ls command to verify msh file
Figure 2.8 mesh command to convert msh file in poly mesh file
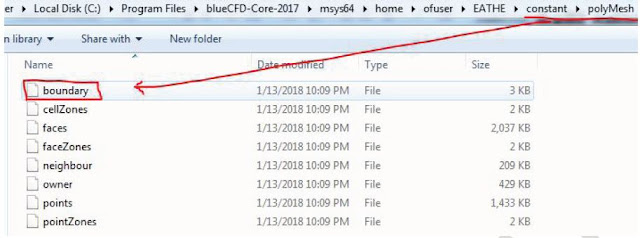
This command create a sub-folder named polymesh in sub-folder constant which we create in starting phase of problem. (see the following figure )
In polymesh folder various files are created. These files have geometry information of EATHE.msh but our consideration is on boundary file (red highlighted in figure)
Figure 2.9 Polymesh folder created by “fluentMeshToFoam” command
Note down all boundary names created from msh file can be see by open the boundary file available in polymesh folder using word-pad/notepad (see the following figure)
Figure 2.10 Boundary name use in 0 subdirectory
Boundary Conditions
After creation of polymesh in constant folder, its time to create boundary files in directory 0 created by user in starting part of the problem. The boundary files depend on governing equations which will be solved during numerical simulation, for this problem the main variables(total eight variables) which must be solved are present in the following figure
Figure 2.11 Boundary conditions for present problem
There are large number of boundary conditions are available, which must be provide to boundary conditions for every problems, the selection is depend on type of boundary conditions useful for particular problem. In this tutorial some important boundary conditions are used all detail information is provided in last of this tutorial book. All files are created using note-pad-2 (provided in software package)
Note: We copy these files from tutorial available in open-foam program files (see the following figure)
Figure 2.12 Copy pee-generated files for present problem
Now edit these boundary files as per given details for all boundary conditions:
alphat boundary condition for EATHE problem
/*--------------------------------*- C++ -*----------------------------------*\
| ========= | |
| \\ / F ield | OpenFOAM: The Open Source CFD Toolbox |
| \\ / O peration | Version: 4.0 |
| \\ / A nd | Web: www.OpenFOAM.org |
| \\/ M anipulation | |
\*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class volScalarField;
location "0";
object alphat;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
dimensions [0 2 -1 0 0 0 0];
internalField uniform 2.3039e-5;
boundaryField
{
in
{
type fixedValue;
value $internalField;
}
out
{
type zeroGradient;
}
hs1
{
type alphatJayatillekeWallFunction;
Prt 0.71;
value $internalField;
}
hs2
{
type alphatJayatillekeWallFunction;
Prt 0.71;
value $internalField;
}
hs3
{
type alphatJayatillekeWallFunction;
Prt 0.71;
value $internalField;
}
wall-basement
{
type alphatJayatillekeWallFunction;
Prt 0.71;
value $internalField;
}
frontAndBackPlanes
{
type empty;
}
}
// ************************************************************************* //
Epsilon boundary condition for EATHE problem
/*--------------------------------*- C++ -*----------------------------------*\
| ========= | |
| \\ / F ield | OpenFOAM: The Open Source CFD Toolbox |
| \\ / O peration | Version: 4.0 |
| \\ / A nd | Web: www.OpenFOAM.org |
| \\/ M anipulation | |
\*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class volScalarField;
location "0";
object epsilon;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
dimensions [0 2 -3 0 0 0 0];
internalField uniform 5e-5;
boundaryField
{
in
{
type fixedValue;
value $internalField;
}
out
{
type zeroGradient;
}
hs1
{
type epsilonWallFunction;
value $internalField;
}
hs2
{
type epsilonWallFunction;
value $internalField;
}
hs3
{
type epsilonWallFunction;
value $internalField;
}
wall-basement
{
type epsilonWallFunction;
value $internalField;
}
frontAndBackPlanes
{
type empty;
}
}
// ************************************************************************* //
K boundary condition for EATHE problem
/*--------------------------------*- C++ -*----------------------------------*\
| ========= | |
| \\ / F ield | OpenFOAM: The Open Source CFD Toolbox |
| \\ / O peration | Version: 4.0 |
| \\ / A nd | Web: www.OpenFOAM.org |
| \\/ M anipulation | |
\*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class volScalarField;
location "0";
object k;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
dimensions [0 2 -2 0 0 0 0];
internalField uniform 1e-4;
boundaryField
{
in
{
type fixedValue;
value $internalField;
}
out
{
type zeroGradient;
}
hs1
{
type kqRWallFunction;
value $internalField;
}
hs2
{
type kqRWallFunction;
value $internalField;
}
hs3
{
type kqRWallFunction;
value $internalField;
}
wall-basement
{
type kqRWallFunction;
value $internalField;
}
frontAndBackPlanes
{
type empty;
}
}
// ************************************************************************* //
Nut boundary condition for EATHE problem
/*--------------------------------*- C++ -*----------------------------------*\
| ========= | |
| \\ / F ield | OpenFOAM: The Open Source CFD Toolbox |
| \\ / O peration | Version: 4.0 |
| \\ / A nd | Web: www.OpenFOAM.org |
| \\/ M anipulation | |
\*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class volScalarField;
location "0";
object nut;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
dimensions [0 2 -1 0 0 0 0];
internalField uniform 0.1;
boundaryField
{
in
{
type fixedValue;
value $internalField;
}
out
{
type zeroGradient;
}
hs1
{
type nutkWallFunction;
value uniform 0;
}
hs2
{
type nutkWallFunction;
value uniform 0;
}
hs3
{
type nutkWallFunction;
value uniform 0;
}
wall-basement
{
type nutkWallFunction;
value uniform 0;
}
frontAndBackPlanes
{
type empty;
}
}
// ************************************************************************* //
P boundary condition for EATHE problem
/*--------------------------------*- C++ -*----------------------------------*\
| ========= | |
| \\ / F ield | OpenFOAM: The Open Source CFD Toolbox |
| \\ / O peration | Version: 4.0 |
| \\ / A nd | Web: www.OpenFOAM.org |
| \\/ M anipulation | |
\*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class volScalarField;
object p;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
dimensions [0 2 -2 0 0 0 0];
internalField uniform 100000;
boundaryField
{
in
{
type zeroGradient;
}
out
{
type fixedValue;
value $internalField;
}
hs1
{
type zeroGradient;
}
hs2
{
type zeroGradient;
}
hs3
{
type zeroGradient;
}
wall-basement
{
type zeroGradient;
}
frontAndBackPlanes
{
type empty;
}
}
// ************************************************************************* //
P_rgh boundary condition for EATHE problem
/*--------------------------------*- C++ -*----------------------------------*\
| ========= | |
| \\ / F ield | OpenFOAM: The Open Source CFD Toolbox |
| \\ / O peration | Version: 4.0 |
| \\ / A nd | Web: www.OpenFOAM.org |
| \\/ M anipulation | |
\*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class volScalarField;
object p_rgh;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
dimensions [0 2 -2 0 0 0 0];
internalField uniform 100000;
boundaryField
{
in
{
type fixedValue;
value $internalField;
}
out
{
type fixedValue;
value $internalField;
}
hs1
{
type zeroGradient;
}
hs2
{
type zeroGradient;
}
hs3
{
type zeroGradient;
}
wall-basement
{
type zeroGradient;
}
frontAndBackPlanes
{
type empty;
}
}
// ************************************************************************* //
T boundary condition for EATHE problem
/*--------------------------------*- C++ -*----------------------------------*\
| ========= | |
| \\ / F ield | OpenFOAM: The Open Source CFD Toolbox |
| \\ / O peration | Version: 4.0 |
| \\ / A nd | Web: www.OpenFOAM.org |
| \\/ M anipulation | |
\*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class volScalarField;
object T;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
dimensions [0 0 0 1 0 0 0];
internalField uniform 310;
boundaryField
{
in
{
type fixedValue;
value uniform 320;
}
out
{
type zeroGradient;
}
hs1
{
type fixedValue;
value uniform 300;
}
hs2
{
type fixedValue;
value uniform 300;
}
hs3
{
type fixedValue;
value uniform 300;
}
wall-basement
{
type fixedValue;
value uniform 300;
}
frontAndBackPlanes
{
type empty;
}
}
// ************************************************************************* //
U boundary condition for EATHE problem
/*--------------------------------*- C++ -*----------------------------------*\
| ========= | |
| \\ / F ield | OpenFOAM: The Open Source CFD Toolbox |
| \\ / O peration | Version: 4.0 |
| \\ / A nd | Web: www.OpenFOAM.org |
| \\/ M anipulation | |
\*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class volVectorField;
object U;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
dimensions [0 1 -1 0 0 0 0];
internalField uniform (0 0 0);
boundaryField
{
in
{
type fixedValue;
value uniform (0 -3 0);
}
out
{
type inletOutlet;
inletValue uniform (0 0 0);
value uniform (0 0 0);
}
hs1
{
type noSlip;
}
hs2
{
type noSlip;
}
hs3
{
type noSlip;
}
wall-basement
{
type noSlip;
}
frontAndBackPlanes
{
type empty;
}
}
// ************************************************************************* //
Fluid Flow Properties (Transport and Turbulence)
These properties are present in directory constant where polymesh is available, the process is same like previous section. For simplicity copy these files from tutorial available in open-foam program files path for selected solver.
Source code for g
/*--------------------------------*- C++ -*----------------------------------*\
| ========= | |
| \\ / F ield | OpenFOAM: The Open Source CFD Toolbox |
| \\ / O peration | Version: 5 |
| \\ / A nd | Web: www.OpenFOAM.org |
| \\/ M anipulation | |
\*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class uniformDimensionedVectorField;
location "constant";
object g;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
dimensions [0 1 -2 0 0 0 0];
value (0 -9.81 0);
// ************************************************************************* //
Source code for Transport Properties
/*--------------------------------*- C++ -*----------------------------------*\
| ========= | |
| \\ / F ield | OpenFOAM: The Open Source CFD Toolbox |
| \\ / O peration | Version: 5 |
| \\ / A nd | Web: www.OpenFOAM.org |
| \\/ M anipulation | |
\*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class dictionary;
object transportProperties;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
transportModel Newtonian;
// Laminar viscosity
nu [0 2 -1 0 0 0 0] 1e-05;
// Thermal expansion coefficient
beta [0 0 0 -1 0 0 0] 3e-03;
// Reference temperature
TRef [0 0 0 1 0 0 0] 300;
// Laminar Prandtl number
Pr [0 0 0 0 0 0 0] 0.7;
// Turbulent Prandtl number
Prt [0 0 0 0 0 0 0] 0.85;
// ************************************************************************* //
Source code for Turbulence Properties
/*--------------------------------*- C++ -*----------------------------------*\
| ========= | |
| \\ / F ield | OpenFOAM: The Open Source CFD Toolbox |
| \\ / O peration | Version: 5 |
| \\ / A nd | Web: www.OpenFOAM.org |
| \\/ M anipulation | |
\*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class dictionary;
location "constant";
object turbulenceProperties;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
simulationType RAS;
RAS
{
RASModel kEpsilon;
turbulence on;
printCoeffs on;
}
// ************************************************************************* //
Time/Solver (Input-Output)
Like other CFD software, Open-Foam is also required time size as per requirement of problem. This task is fulfill by creating controlDict file in directory “system”
/*--------------------------------*- C++ -*----------------------------------*\
| ========= | |
| \\ / F ield | OpenFOAM: The Open Source CFD Toolbox |
| \\ / O peration | Version: 5 |
| \\ / A nd | Web: www.OpenFOAM.org |
| \\/ M anipulation | |
\*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class dictionary;
location "system";
object controlDict;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
application buoyantBoussinesqPimpleFoam;
startFrom startTime;
startTime 0;
stopAt endTime;
endTime 20;
deltaT 0.004;
writeControl timeStep;
writeInterval 200;
purgeWrite 0;
writeFormat ascii;
writePrecision 6;
writeCompression off;
timeFormat general;
timePrecision 6;
runTimeModifiable true;
adjustTimeStep yes;
maxCo 1.0;
// ************************************************************************* //
Numerical Schemes
The numerical schemes are defined in file fvSchemes available in directory system created by user in starting phase of problem.
/*--------------------------------*- C++ -*----------------------------------*\
| ========= | |
| \\ / F ield | OpenFOAM: The Open Source CFD Toolbox |
| \\ / O peration | Version: 5 |
| \\ / A nd | Web: www.OpenFOAM.org |
| \\/ M anipulation | |
\*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class dictionary;
location "system";
object fvSchemes;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
ddtSchemes
{
default Euler;
}
gradSchemes
{
default Gauss linear;
}
divSchemes
{
default none;
div(phi,U) Gauss upwind;
div(phi,T) Gauss upwind;
div(phi,k) Gauss upwind;
div(phi,epsilon) Gauss upwind;
div(phi,R) Gauss upwind;
div(R) Gauss linear;
div((nuEff*dev2(T(grad(U))))) Gauss linear;
}
laplacianSchemes
{
default Gauss linear uncorrected;
}
interpolationSchemes
{
default linear;
}
snGradSchemes
{
default uncorrected;
}
// ************************************************************************* //
Solution Control
Solution is controlled by making file fvSolution in directory system
/*--------------------------------*- C++ -*----------------------------------*\
| ========= | |
| \\ / F ield | OpenFOAM: The Open Source CFD Toolbox |
| \\ / O peration | Version: 5 |
| \\ / A nd | Web: www.OpenFOAM.org |
| \\/ M anipulation | |
\*---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class dictionary;
location "system";
object fvSolution;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
solvers
{
p_rgh
{
solver PCG;
preconditioner DIC;
tolerance 1e-8;
relTol 0.01;
}
p_rghFinal
{
$p_rgh;
relTol 0;
}
"(U|T|k|epsilon|R)"
{
solver PBiCGStab;
preconditioner DILU;
tolerance 1e-6;
relTol 0.1;
}
"(U|T|k|epsilon|R)Final"
{
$U;
relTol 0;
}
}
PIMPLE
{
momentumPredictor no;
nOuterCorrectors 1;
nCorrectors 2;
nNonOrthogonalCorrectors 0;
pRefCell 0;
pRefValue 0;
}
relaxationFactors
{
equations
{
"(U|T|k|epsilon|R)" 1;
"(U|T|k|epsilon|R)Final" 1;
}
}
// ************************************************************************* //
Solver Running
After created the all desired source files for present problem only last step is to run the solver by provide the command “” (see the following figure)
Figure 2.13 command for run the solver
As the solver is running it must be take care of Courant number issue
Figure 2.14 Solver running in open-foam code
After successful ending of solver running condition, various sub-folders are created in user directory EATHE for different time conditions
Post-Processing
In this step solved problem is analysis by using para-foam software available with open-foam software. To run this software run command “para-foam” in terminal of open-foam software. It must take care that terminal selected EATHE folder before run this command.
Figure 2.15 para-foam for post-processing of problem
Para-view is very large software for post-processing of CFD simulation files so in this tutorial we skip this software at this stage. Only some important results are present here.
Temperature Contours
Velocity Contours
This offering is not approved or endorsed by OpenCFD Limited, producer and distributor of the OpenFOAM software and owner of the OPENFOAM® and OpenCFD® trade marks.
END
















Comments
Post a Comment